

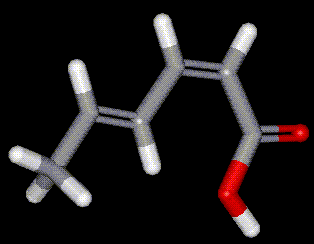
 Occurs naturally in fruit, used as a preservative it inhibits fungal growth but allows for bacterial activity, hence is useful for cheese. Obtained from the berries of mountain ash. Sorbic acid is used in conjunction with sulphur dioxide in wine making, without SO2 bacteria cause reduction of sorbic acid to sorbyl alcohol which converts to a foul smelling ether. Also used as a preservative in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Sorbic acid had a conjugated system of double bonds which makes it susceptible to nucleophilic
attack, sometimes giving mutagenic products. Food labelled as containing E200 may actually contain sodium, potassium or calcium sorbate instead (E201, E202 and E203 respectively).
Occurs naturally in fruit, used as a preservative it inhibits fungal growth but allows for bacterial activity, hence is useful for cheese. Obtained from the berries of mountain ash. Sorbic acid is used in conjunction with sulphur dioxide in wine making, without SO2 bacteria cause reduction of sorbic acid to sorbyl alcohol which converts to a foul smelling ether. Also used as a preservative in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Sorbic acid had a conjugated system of double bonds which makes it susceptible to nucleophilic
attack, sometimes giving mutagenic products. Food labelled as containing E200 may actually contain sodium, potassium or calcium sorbate instead (E201, E202 and E203 respectively).| Other names: | 2,4-Hexadienoic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C6 H8 O2 |
| CAS No: | 110-44-1 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 134 C |
| Boiling point: | 228 C |
| Other information: | May act as an irritant. |
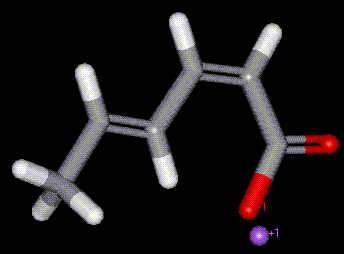 Sodium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. Plays a similar role in food preservation as sorbic acid, E200.
Sodium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. Plays a similar role in food preservation as sorbic acid, E200.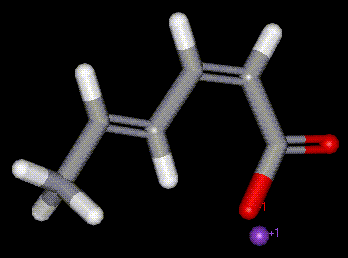 Potassium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. Plays a similar role in food preservation as sorbic acid, E200. More soluble than sorbic acid.
Potassium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. Plays a similar role in food preservation as sorbic acid, E200. More soluble than sorbic acid.| Other names: | 2,4-hexadienoic acid potassium salt |
| Molecular formula: | CH3CH:CHCH:CHCOOK |
| CAS No: | 24634-61-5 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 270 C |
| Other information: | May act as an irritant. |
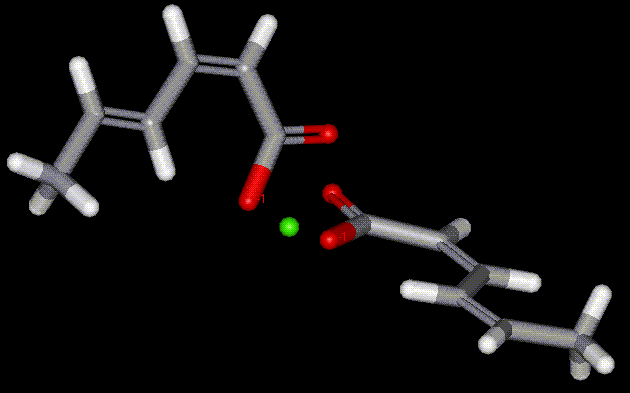 The calcium salt of sorbic acid. An antifungal antibacterial preservative.
The calcium salt of sorbic acid. An antifungal antibacterial preservative. Occurs naturally in a variety of produce, but is also industrially synthesised. Benzoic acid is also used in the manufacture of plasticisers, resin coatings and caprolactam. It is an antiseptic, antifungal, antipyretic agent, and can be used as an alkalimetric standard.
Occurs naturally in a variety of produce, but is also industrially synthesised. Benzoic acid is also used in the manufacture of plasticisers, resin coatings and caprolactam. It is an antiseptic, antifungal, antipyretic agent, and can be used as an alkalimetric standard.| Other names: | benzene carboxylic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C6H5COOH |
| CAS No: | 65-85-0 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Melting point: | 122 C |
| Boiling point: | 249 C |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed, may irritate the eyes and lungs. |
 The sodium salt of benzoic acid, sodium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role.
The sodium salt of benzoic acid, sodium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role.| Other names: | sodium benzoic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C6H5COONa |
| CAS No: | 532-32-1 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Other information: | may cause skin irritation, harmful if swallowed. |
 The potassium salt of benzoic acid, potassium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role.
The potassium salt of benzoic acid, potassium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role.| Molecular formula: | C7 H6 O2 . K (Derived) |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline solid |
 The calcium salt of benzoic acid, calcium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role.
The calcium salt of benzoic acid, calcium benzoate fulfils an antibacterial and antifungal role. A derivative of benzoic acid. Has anaesthetic properties and may cause numbness to the mouth.
A derivative of benzoic acid. Has anaesthetic properties and may cause numbness to the mouth. The sodium salt of ethyl para-hydroxybenzoate, used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative, also has anaesthetic effects.
The sodium salt of ethyl para-hydroxybenzoate, used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative, also has anaesthetic effects. Synthesised from benzoic acid (E200). Antimicrobial, may be a numbing effect on the mouth.
Synthesised from benzoic acid (E200). Antimicrobial, may be a numbing effect on the mouth. The sodium salt of propyl para-hydroxybenzoate, E217 is produced from benzoic acid and is an antimicrobial preservative. May cause irritation to sensitive skin.
The sodium salt of propyl para-hydroxybenzoate, E217 is produced from benzoic acid and is an antimicrobial preservative. May cause irritation to sensitive skin. Synthesised from benzoic acid, methyl para-hydroxybenzoate is a antimicrobial agent.
Synthesised from benzoic acid, methyl para-hydroxybenzoate is a antimicrobial agent.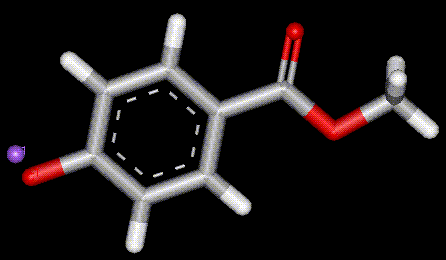 The sodium salt of E218, sodium methyl para-hydroxybenzoate is primarily an antifungal agent. May cause irritation to the skin.
The sodium salt of E218, sodium methyl para-hydroxybenzoate is primarily an antifungal agent. May cause irritation to the skin.  Occurs naturally in the atmosphere and as a pollutant gas from combustion processes, sulphur dioxide is implicated in formation of acid rain and has a choking odour. It is commercially produced either by combustion of sulphur, hydrogen sulphide or gypsum. Most industrially produced sulphur dioxide is used in the production of sulphuric acid, but it is also used as a bleach, disinfectant and refrigerant. Used as a preservative in wine for its antibacterial properties, and as a bleaching agent in flour. Sulphur dioxide may be used to fumigate fruit and vegetables to extend their shelf life. Sulphur dioxide may not be used for foods containing a significant amount of thiamine, as this is destroyed by the gas. Similar functional properties are displayed by the sulphites (E221-E227).
Occurs naturally in the atmosphere and as a pollutant gas from combustion processes, sulphur dioxide is implicated in formation of acid rain and has a choking odour. It is commercially produced either by combustion of sulphur, hydrogen sulphide or gypsum. Most industrially produced sulphur dioxide is used in the production of sulphuric acid, but it is also used as a bleach, disinfectant and refrigerant. Used as a preservative in wine for its antibacterial properties, and as a bleaching agent in flour. Sulphur dioxide may be used to fumigate fruit and vegetables to extend their shelf life. Sulphur dioxide may not be used for foods containing a significant amount of thiamine, as this is destroyed by the gas. Similar functional properties are displayed by the sulphites (E221-E227). | Other names: | sulphur superoxide |
| Molecular formula: | S O2 |
| CAS No: | 7446-09-5 |
| Physical appearance: | Colourless gas |
| Melting point: | -73 C |
| Boiling point: | -10 C |
| Other information: | corrosive when wet, toxic in high concentrations. Sulphurous acid, produced when sulphur dioxide in food is dissolved, may cause gastric irritation. |
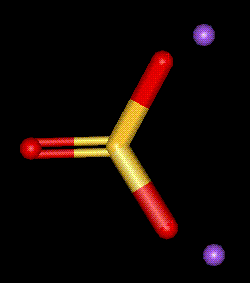 The sodium salt of sulphurous acid. Used to sterilise fermentation equipment and food containers, as well as for its antimicrobial properties. Generally meat, cereals and dairy products may not be treated with E221 as it destroys thiamine content. Over exposure to sulphites in food may cause an asthmatic attack, or cause gastric irritation.
The sodium salt of sulphurous acid. Used to sterilise fermentation equipment and food containers, as well as for its antimicrobial properties. Generally meat, cereals and dairy products may not be treated with E221 as it destroys thiamine content. Over exposure to sulphites in food may cause an asthmatic attack, or cause gastric irritation.| Other names: | anhydrous sodium sulfite, sodium sulphite |
| Molecular formula: | Na2 S O3 |
| CAS No: | 7757-83-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Other information: | Moisture and air sensitive. Possible mutagen. Harmful by inhalation, ingestion and skin contact. Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause allergic reaction. |
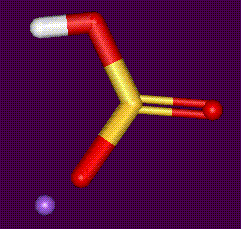 Another sodium salt of sulphurous acid, sulphur dioxide may be released from food containing sulphites. May induce an attack in asthmatics, or cause gastric irritation due to this release of sulphur dioxide. Thiamine is destroyed by sulphites. Sulphites are also used as bleaching agents.
Another sodium salt of sulphurous acid, sulphur dioxide may be released from food containing sulphites. May induce an attack in asthmatics, or cause gastric irritation due to this release of sulphur dioxide. Thiamine is destroyed by sulphites. Sulphites are also used as bleaching agents.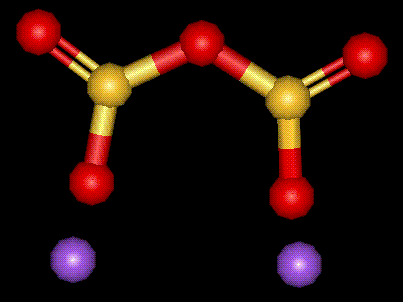 Another sodium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used as an antimicrobial preservative, antioxidant and bleaching agent in food.
Another sodium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used as an antimicrobial preservative, antioxidant and bleaching agent in food.| Other names: | pyrosulphurous acid, disodium salt. |
| Molecular formula: | Na2S2O5 |
| CAS No: | 7681-57-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals with smell of sulphur dioxide |
| Other information: | overexposure may cause an allergic reaction. May cause hypersensitivity reactions in sensitive individuals, especially asthmatics. |
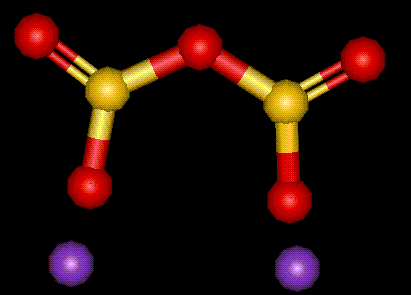 A potassium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used as an antimicrobial preservative, particularly in wine.
A potassium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used as an antimicrobial preservative, particularly in wine.| Other names: | potassium pyrosulfite, pyrosulfurous acid dipotassium salt |
| Molecular formula: | K2S2O5 |
| CAS No: | 16731-55-8 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline solid |
| Other information: | Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. |
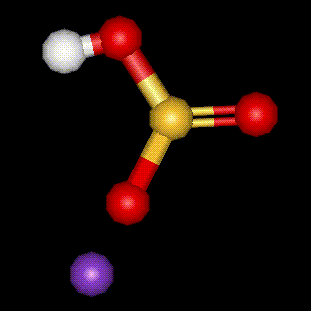 Another potassium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used not only as a food preservative, but also as a firming agent and disinfectant in food preparation.
Another potassium salt of sulphurous acid, see E222. Used not only as a food preservative, but also as a firming agent and disinfectant in food preparation.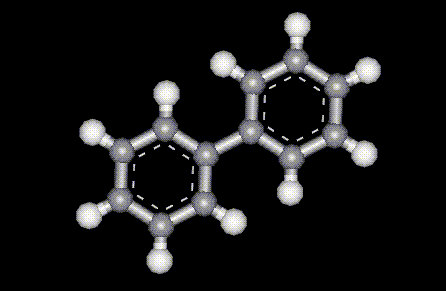 An antifungal derivative of benzene, used to inhibit the growth of mould on citrus fruits.
An antifungal derivative of benzene, used to inhibit the growth of mould on citrus fruits.| Other names: | diphenyl |
| Molecular formula: | C6H5C6H5 |
| CAS No: | 92-52-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white scales with pleasant odour. |
| Melting point: | 70 C |
| Boiling point: | 255 C |
| Other information: | may cause irritation to the skin, eyes and lungs. Ingestion may cause vomiting, headaches, dizziness, gastrointestinal irritation. May cause central nervous system depression in large quantities. |
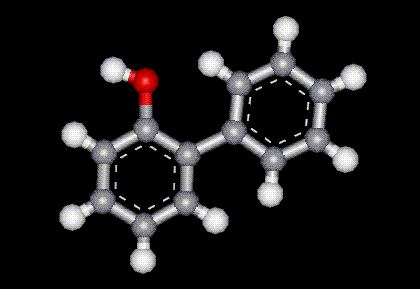 Used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative in food.
Used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative in food.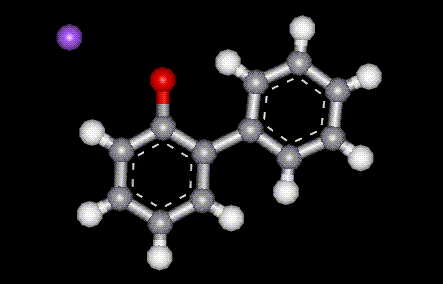 The sodium salt of E231, used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative in food.
The sodium salt of E231, used as an antibacterial and antifungal preservative in food.| Molecular formula: | C10H7N3S |
| Melting point: | 304 C |
| Other information: | Shows teratogenic activity in mice. |
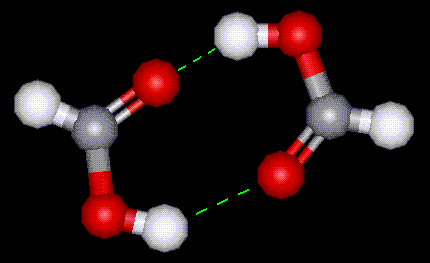 Formic acid is used as a preservative in food, and also in manufacture of leather and preparation of latex rubber. It occurs naturally in ants, is completely soluble in water, and in solution exists as hydrogen-bonded dimers. It is industrially synthesised from carbon monoxide, and is thought to exist in two resonance forms. Formic acid has diuretic properties.
Formic acid is used as a preservative in food, and also in manufacture of leather and preparation of latex rubber. It occurs naturally in ants, is completely soluble in water, and in solution exists as hydrogen-bonded dimers. It is industrially synthesised from carbon monoxide, and is thought to exist in two resonance forms. Formic acid has diuretic properties.| Other names: | formylic acid, hydrogen carboxylic acid, methanoic acid |
| Molecular formula: | CH2O2 |
| CAS No: | 64-18-6 |
| Physical appearance: | Colourless liquid |
| Melting point: | 8.4 C |
| Boiling point: | 100 - 101 C |
| Other information: | Corrosive, causes severe burns. Harmful by inhalation, ingestion and through skin absorption. Readily absorbed through skin. Very destructive of mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract, eyes and skin. Inhalation may be fatal. |
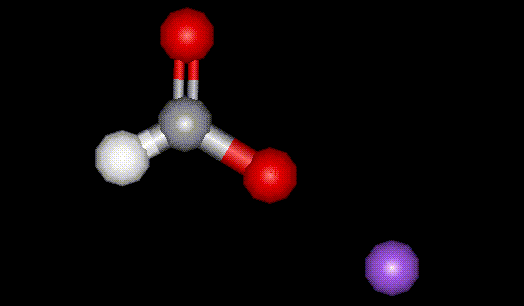 This is the sodium salt of formic acid, E236, formerly used as a diuretic.
This is the sodium salt of formic acid, E236, formerly used as a diuretic.| Other names: | formic acid sodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | C H O2 Na |
| CAS No: | 141-53-7 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals |
| Melting point: | 260 C |
| Other information: | Skin, eye and respiratory tract irritant. |
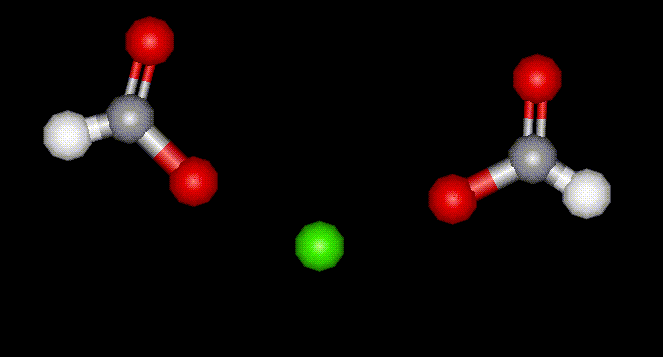 This is the calcium salt of formic acid, E236, formerly used as a diuretic.
This is the calcium salt of formic acid, E236, formerly used as a diuretic.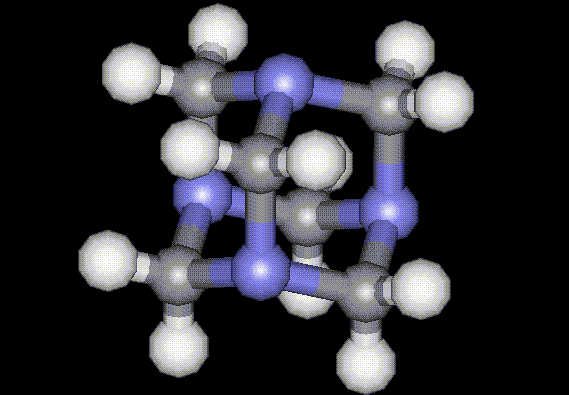 Hexamine is an antibacterial agent and a physiologically active compound due to the presence of N. It is manufactured using formaldehyde and ammonia, and prolonged ingestion may result in stomach upsets. Hexamine may be carcinogenic.
Hexamine is an antibacterial agent and a physiologically active compound due to the presence of N. It is manufactured using formaldehyde and ammonia, and prolonged ingestion may result in stomach upsets. Hexamine may be carcinogenic.| Other names: | methenamine, urotropin, HMTA, hexaform |
| Molecular formula: | (CH2)6N4 |
| CAS No: | 100-97-0 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Other information: | May act as a skin, eye or respiratory irritant. |
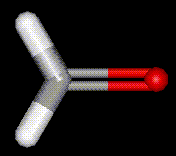 Formaldehyde is the most important industrial aldehyde with about 8 billion pounds of formaldehyde being made each year. The industrial synthesis of formaldehyde involves methanol. The incomplete combustion of organic compounds results in formaldehyde formation, hence smoked foods are preserved not only by phenolic substances present in the smoke, by the formaldehyde coating. It is also used as a disinfectant and a fungicide. Its main application is in the preparation of phenolic resins (or phenol-formaldehyde copolymers, e.g. bakelite). Formaldehyde is also used in the preparation of ribose.
Formaldehyde is the most important industrial aldehyde with about 8 billion pounds of formaldehyde being made each year. The industrial synthesis of formaldehyde involves methanol. The incomplete combustion of organic compounds results in formaldehyde formation, hence smoked foods are preserved not only by phenolic substances present in the smoke, by the formaldehyde coating. It is also used as a disinfectant and a fungicide. Its main application is in the preparation of phenolic resins (or phenol-formaldehyde copolymers, e.g. bakelite). Formaldehyde is also used in the preparation of ribose.| Other names: | formalin, formic aldehyde, methylene oxide, oxomethane, paraform |
| Molecular formula: | CH2O |
| CAS No: | 50-00-0 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless liquid |
| Other information: | Causes burns. Very toxic by inhalation, ingestion and through skin absorption. Readily absorbed through skin. Possible cancer hazard. Mutagen. May cause damage to kidneys. May cause allergic reactions. May cause sensitisation. May cause heritable genetic damage. Lachrymator. Very destructive of mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract, eyes and skin. |
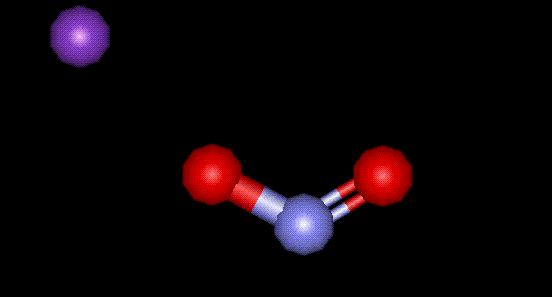 Potassium nitrite is the potassium salt of nitrous acid and is used as a curing agent and preservative in meat. Excessive ingestion may result in such high concentrations of nitrites in the bloodstream that reduced concentrations of oxygen are carried by haemoglobin in red blood cells, leading to dizziness and headaches. Nitrites may also form nitrosamines in the stomach, thought to be carcinogenic agents. Potassium nitrite inhibits the growth of bacteria responsible for botulism, retards development of rancidity, and preserves flavours. Less than 10% of nitrate (nitrite) intake is from cured meats, with the rest coming from mainly root vegetables.
Potassium nitrite is the potassium salt of nitrous acid and is used as a curing agent and preservative in meat. Excessive ingestion may result in such high concentrations of nitrites in the bloodstream that reduced concentrations of oxygen are carried by haemoglobin in red blood cells, leading to dizziness and headaches. Nitrites may also form nitrosamines in the stomach, thought to be carcinogenic agents. Potassium nitrite inhibits the growth of bacteria responsible for botulism, retards development of rancidity, and preserves flavours. Less than 10% of nitrate (nitrite) intake is from cured meats, with the rest coming from mainly root vegetables.| Other names: | nitrous acid potassium salt |
| Molecular formula: | KNO2 |
| CAS No: | 7758-09-0 |
| Physical appearance: | white to yellow crystals |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed. Laboratory tests suggest that this material may be mutagenic or teratogenic. Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. |
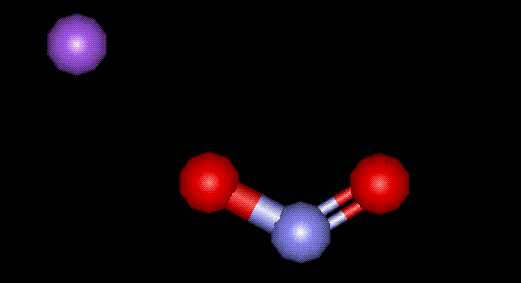 Sodium nitrite is the sodium salt of nitrous acid. See E249.
Sodium nitrite is the sodium salt of nitrous acid. See E249.| Other names: | nitrous acid sodium salt, diazoting salts |
| Molecular formula: | Na NO2 |
| CAS No: | 7632-00-0 |
| Physical appearance: | white to light yellow granules or powder |
| Melting point: | 271 C |
| Boiling point: | 320 C |
| Other information: | Toxic. May be fatal if swallowed. Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. Some laboratory experiments suggest that this material may act as a carcinogen. |
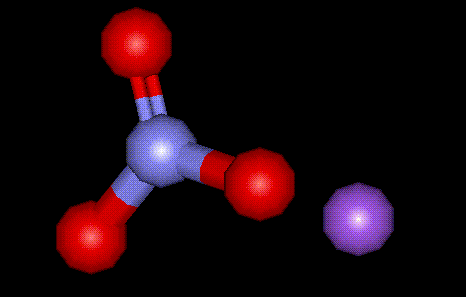 Sodium nitrate is a natural mineral, occurring in great abundance in the Atacama desert (hence the name Chile saltpetre). It is used as a preservative and curing agent in meat. See E249, potassium nitrite.
Sodium nitrate is a natural mineral, occurring in great abundance in the Atacama desert (hence the name Chile saltpetre). It is used as a preservative and curing agent in meat. See E249, potassium nitrite.| Other names: | Chile saltpetre, cubic nitre, nitric acid sodium salt |
| Molecular formula: | Na NO3 |
| CAS No: | 7631-99-4 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless crystals or white powder |
| Melting point: | 306 C |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed or inhaled. Skin, eye and respiratory irritant. |
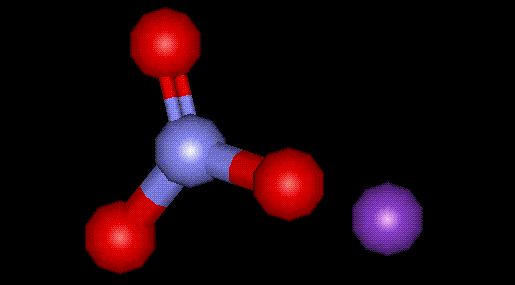 Potassium nitrate is a naturally occurring mineral used as a preservative and curing agent in meat. It is artificially manufactured by the reaction of potassium chloride with nitric acid. See E249, potassium nitrite. Potassium nitrate is used in fireworks as well as fertilisers.
Potassium nitrate is a naturally occurring mineral used as a preservative and curing agent in meat. It is artificially manufactured by the reaction of potassium chloride with nitric acid. See E249, potassium nitrite. Potassium nitrate is used in fireworks as well as fertilisers.| Other names: | Synonyms: |
| Molecular formula: | KNO3 |
| CAS No: | 7757-79-1 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless crystals or white powder |
| Melting point: | 334 C |
| Boiling point: | 400 C (decomposes) |
| Other information: | Harmful if swallowed. May cause reproductive disorders. |
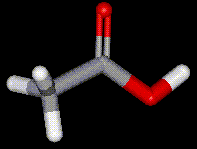 Acetic acid (ethanoic acid) has been used for hundreds of years
Acetic acid (ethanoic acid) has been used for hundreds of years  as a preservative (vinegar, French for "sour wine"). If during the fermentation of grapes or other
fruits, oxygen is allowed into the container, then bacteria convert the ethanol present into ethanoic acid causing the wine to turn sour. Acetic acid may be synthetically produced using methanol carbonylation, acetaldehyde oxidation, or butane/naphtha oxidation. Pure acetic acid is termed "glacial", and is completely miscible with water.
as a preservative (vinegar, French for "sour wine"). If during the fermentation of grapes or other
fruits, oxygen is allowed into the container, then bacteria convert the ethanol present into ethanoic acid causing the wine to turn sour. Acetic acid may be synthetically produced using methanol carbonylation, acetaldehyde oxidation, or butane/naphtha oxidation. Pure acetic acid is termed "glacial", and is completely miscible with water.| Other names: | ethanoic acid |
| Molecular formula: | C2 H4 O2 |
| CAS No: | 64-19-7 |
| Melting point: | 16.7 C |
| Boiling point: | 118 C |
| Other information: | Acetic acid is strongly corrosive and causes serious burns, as well as being a lachrymator. |

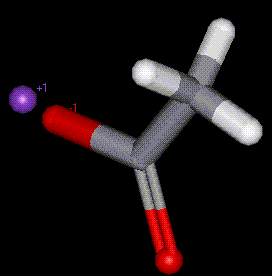 The potassium salt of acetic acid, E260. In industry is used to aid conditioning of fabrics, used in the manufacture of penicillin.
The potassium salt of acetic acid, E260. In industry is used to aid conditioning of fabrics, used in the manufacture of penicillin.
| Other names: | acetic acid potassium salt, potassium ethanoate, ethanoic acid potassium salt |
| Molecular formula: | CH3COOK |
| CAS No: | 127-08-2 |
| Melting point: | 292 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the skin, eyes and lungs. |
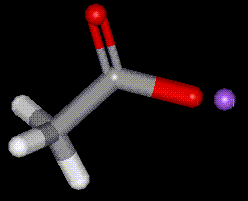 The sodium salt of acetic acid, E260. Acts as a buffer in foods. Technical grade sodium acetate is used as a mordant in dyeing processes, as buffers in petroleum production, and for kidney dialysis processes. In plastic manufacturing it is used as a retarder for some elastomers.
The sodium salt of acetic acid, E260. Acts as a buffer in foods. Technical grade sodium acetate is used as a mordant in dyeing processes, as buffers in petroleum production, and for kidney dialysis processes. In plastic manufacturing it is used as a retarder for some elastomers.| Other names: | sodium acetate (anhydrous) |
| Molecular formula: | CH3COONa |
| CAS No: | 127-09-3 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point: | 324 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the skin, harmful if ingested |
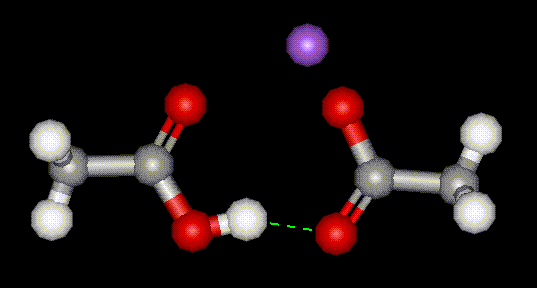 A vinegar used as a mould inhibitor in snack foods and bread, as a flavour enhancer in breads, cakes, cheese and snack food. Technical grade sodium hydrogen acetate is used as a buffer in petroleum production.
A vinegar used as a mould inhibitor in snack foods and bread, as a flavour enhancer in breads, cakes, cheese and snack food. Technical grade sodium hydrogen acetate is used as a buffer in petroleum production.| CAS No: | 126-96-5 |
| Chemical formula: | C4H7O4Na |
| Other information: | a compound of acetic acid and sodium acetate |
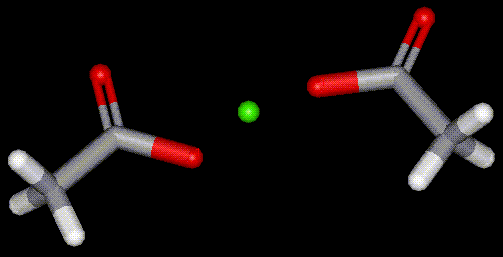 Calcium acetate is used in food as a thickening agent (cake mixtures, puddings, pie fillings), as a buffer in controlling the pH of food during processing, as a preservative to prevent microbial growth, and as a calcium supplement in pet products. In other areas of industry calcium acetate is used in dyeing and printing.
Calcium acetate is used in food as a thickening agent (cake mixtures, puddings, pie fillings), as a buffer in controlling the pH of food during processing, as a preservative to prevent microbial growth, and as a calcium supplement in pet products. In other areas of industry calcium acetate is used in dyeing and printing.| Other names: | calcium acetate monohydrate, calcium diacetate |
| Molecular formula: | Ca C4 H6 O4 |
| CAS No: | 5743-26-0 or 62-54-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals or powder |
| Other information: | May cause eye, skin or respiratory irritation. Mutagenic effects noted in laboratory tests. |
| Molecular formula: | CH3COONH4 |
| CAS No: | 631-61-8 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals |
| Melting point: | 114 C (dec.) |
| Other information: | May be harmful by inhalation or ingestion. Irritant. |
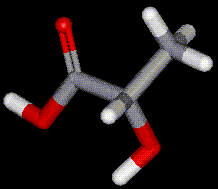 Lactic acid is a naturally occurring compound present in sour milk, molasses and fruit. Lactic acid is produced commercially by fermentation of carbohydrates in the presence of lactic acid bacteria. Lactic acid occurs naturally in the blood (lactates) when glycogen is broken down in the muscles.
Lactic acid is a naturally occurring compound present in sour milk, molasses and fruit. Lactic acid is produced commercially by fermentation of carbohydrates in the presence of lactic acid bacteria. Lactic acid occurs naturally in the blood (lactates) when glycogen is broken down in the muscles.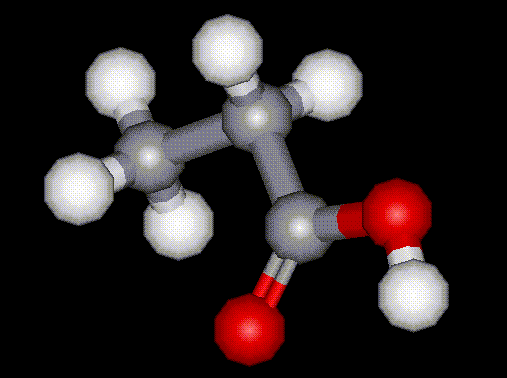 Propionic acid is used as an antifungal agent in food. It is naturally occurring as one of the products of digestion of cellulose in herbivorous animals. It is commercially synthesised from many different methods, including from ethylene, carbon monoxide and steam; or from natural gas.
Propionic acid is used as an antifungal agent in food. It is naturally occurring as one of the products of digestion of cellulose in herbivorous animals. It is commercially synthesised from many different methods, including from ethylene, carbon monoxide and steam; or from natural gas.| Other names: | carboxyethane, ethylformic acid, methylacetic ac |
| Molecular formula: | C2H5COOH |
| CAS No: | 79-09-4 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless oily liquid with a pungent rancid odour |
| Melting point: | -21 C |
| Boiling point: | 141 C |
| Other information: | Corrosive - causes burns. Harmful if swallowed. Liquid may burn eyes. Severe eye and skin irritant. |
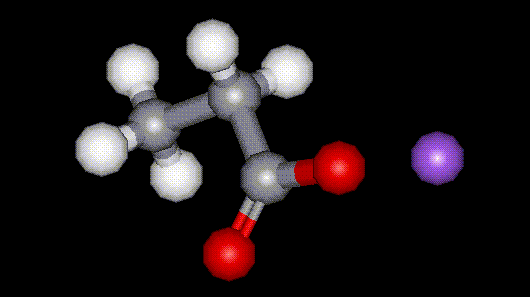 Sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur.
Sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur.| Other names: | propionic acid, sodium salt. |
| Molecular formula: | CH3CH2COONa |
| CAS No: | 137-40-6 |
| Physical appearance: | white powder |
| Melting point: | 285 C |
| Other information: | May irritate the eyes and skin, readily absorbed through the skin. |
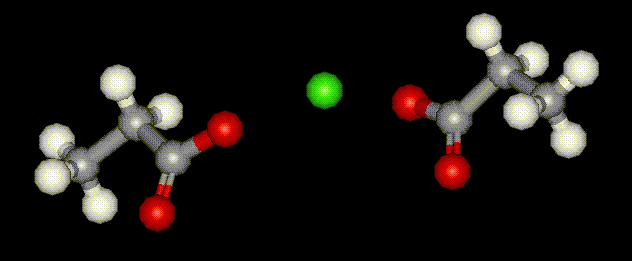 Calcium propionate is the calcium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur.
Calcium propionate is the calcium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur.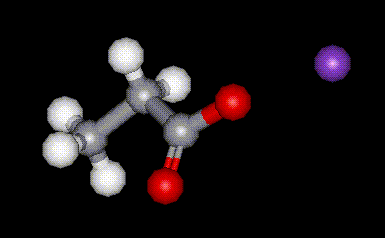 Potassium propionate is the potassium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur.
Potassium propionate is the potassium salt of propionic acid, E280. It is used as an antimicrobial agent in bread to prevent germination of some types of bacteria which causes sticky yellow patches to occur. Boric acid is best known for being an antiseptic, but it is also used in insecticides, leather finishing, paints, soaps, wood preserving, and in ceramics and glass manufacturing. Boric acid is industrially synthesised by treating borax with strong acid. Boric acid forms crystals in which a planar array of BO3 units is joined by unsymmetrical H bonds.
Boric acid is best known for being an antiseptic, but it is also used in insecticides, leather finishing, paints, soaps, wood preserving, and in ceramics and glass manufacturing. Boric acid is industrially synthesised by treating borax with strong acid. Boric acid forms crystals in which a planar array of BO3 units is joined by unsymmetrical H bonds.| Other names: | boracic acid, orthoboric acid, borofax |
| Molecular formula: | H3BO3 |
| CAS No: | 10043-35-3 |
| Physical appearance: | colourless or white odourless crystalline solid |
| Melting point: | 171 C |
| Boiling point: | 300 C (dec.) |
| Other information: | Ingestion is harmful and may be fatal. Harmful by inhalation. Irritant. May cause congenital malformation in the fetus. Laboratory tests with animals suggest this material may cause reproductive disorders. |
| Other names: | borax decahydrate, boricin, disodium tetraborate decahydrate |
| Molecular formula: | B4 Na2 O7 |
| CAS No: | 1303-96-4 |
| Physical appearance: | white crystals |
| Other information: | Possible risk that this may cause reproductive disorders, based on tests with laboratory animals. Eye and skin irritant. Harmful by ingestion. May be harmful by inhalation. |

| Molecular formula: | Cl2 |
| CAS No: | 7782-50-5 |
| Physical appearance: | light greenish-yellow gas with an irritating odour |
| Melting point: | -101 C |
| Boiling point: | -34 C |
| Other information: | Toxic by inhalation, ingestion and through skin contact. Inhalation can cause serious lung damage and may be fatal. 1000ppm (0.1%) is likely to be fatal after a few deep breaths, and half that concentration fatal after a few minutes. May irritate or burn skin. |
| Other names: | chlorine oxide |
| Molecular formula: | Cl O2 |
| CAS No: | 10049044 |
| Melting point: | -59.5 C |
| Boiling point: | 9.9 C |
| Other information: | Corrosive, Severe respiratory and eye irritant. |
 Lysozyme is obtained from chicken egg white.
Lysozyme is obtained from chicken egg white.| CAS No: | 12650-88-3 |
| Physical appearance: | solid |
| Other information: | May be harmful by inhalation or ingestion, or act as an irritant. |